SHARE THIS ARTICLE
What Are Layer3 Blockchains & How Do They Improve Scalability

Blockchain-based decentralized applications (dApps) offer innovative solutions across various industries – from secure data storage to automated financial transactions. This underscores the undeniable promise of blockchain technology and Web3 development services. However, scalability still remains a significant challenge. Popular dApps often experience slow transaction times, affecting user experience and limiting widespread adoption.
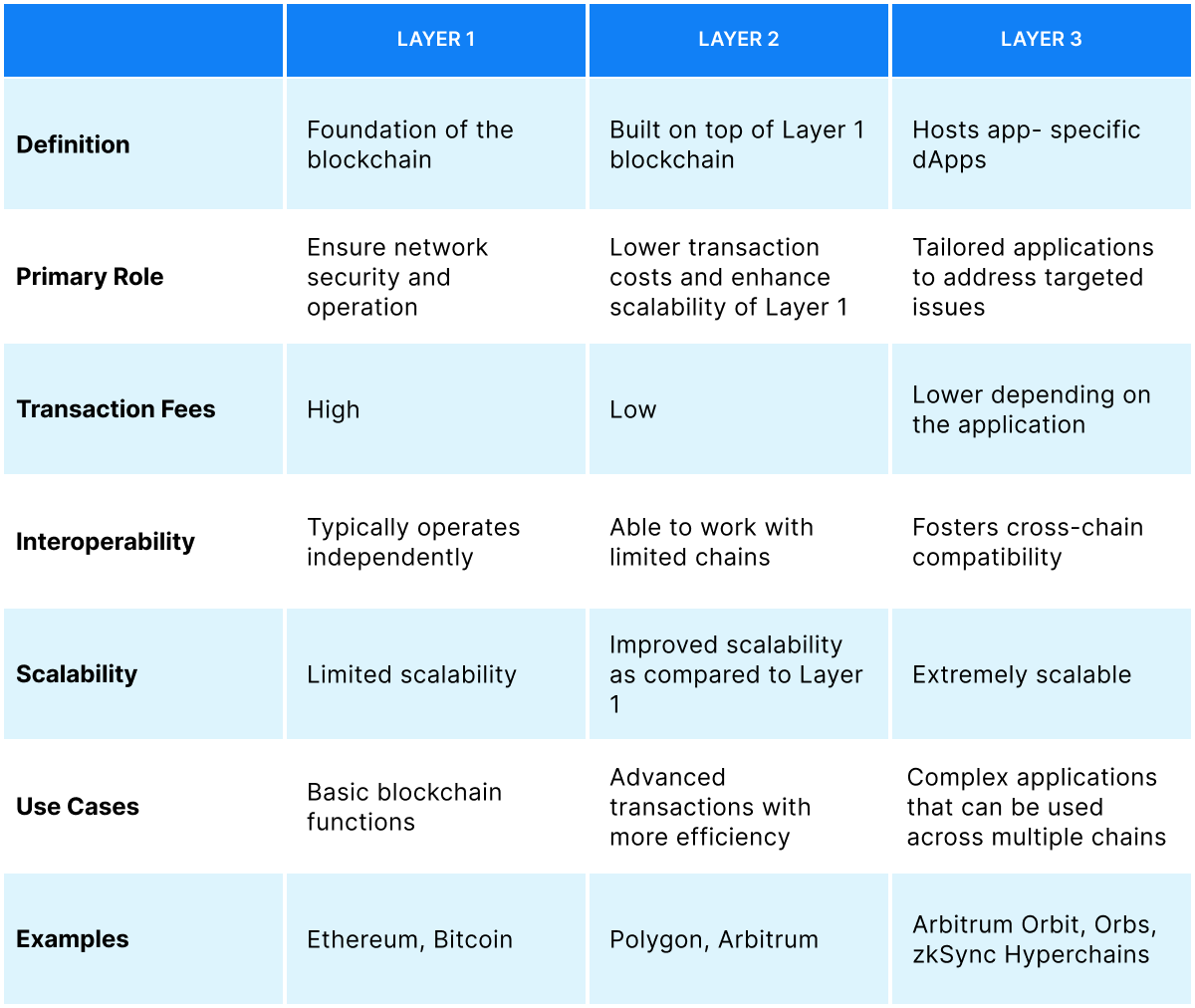
The primary reason for this bottleneck is the limitations in how current blockchains process information. Layer1 blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum 1.0, act as the foundation, offering security and immutability. However, they rely on slow consensus mechanisms, which restricts the number of transactions they can handle per second.
To address this, Layer 2 scaling solutions emerged. These act as overlays on Layer 1, offloading transaction processing and increasing throughput. However, Layer 2 solutions often introduce complexities and may not guarantee the same level of security as Layer 1.
This issue warrants a comprehensive solution and Layer 3 blockchains show immense promise. As an innovative solution, L3s are designed to bridge the gap between security and scalability. Layer3 scaling solutions empower the dApps, encouraging mass adoption.
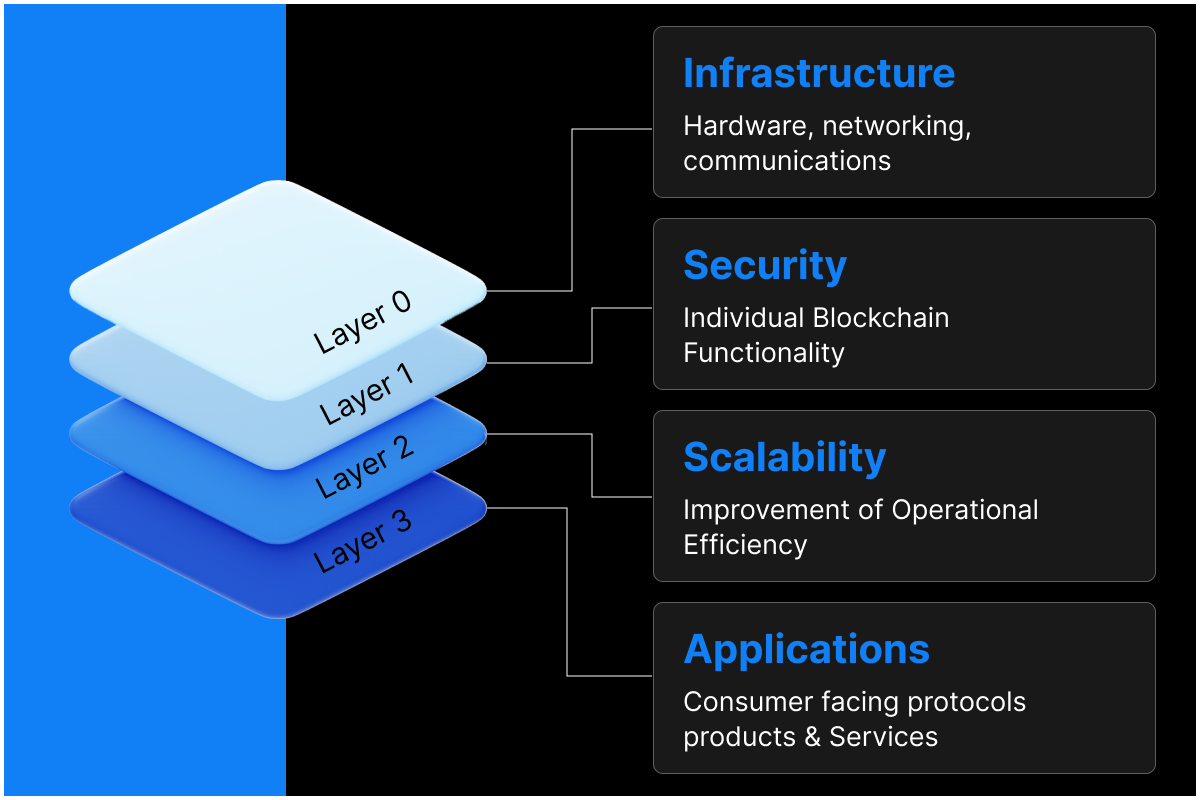
Understanding the Difference Between the Difference Layers of Blockchain
To understand Layer 3 blockchains, it's crucial to grasp the existing layered architecture of blockchain technology.
Layer 1- The Base Layer
Layer 1 blockchains are the foundation of the blockchain ecosystem. They provide the core functionalities of a blockchain.
-
Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, ensuring trust and transparency.
-
Security: Transactions are cryptographically secured and tamper-proof.
-
Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered.
However, Layer 1 blockchains often struggle with scalability. Their consensus mechanisms, which ensure the validity of transactions, can be computationally intensive, limiting the number of transactions they can process per second. This results in slow transaction times, especially for busy networks.
Layer 2 – Scaling the Base Layer
Layer2 scaling solutions address the limitations of Layer 1 by offloading some of the processing burden. They operate on top of Layer 1, inheriting its security but offering faster transaction throughput. Here are two common types of Layer 2 solutions:
-
Sidechains: These are independent blockchains that operate alongside the main blockchain. Transactions are batched and transferred to the main chain periodically, reducing congestion on Layer 1.
-
Rollups: These process transactions off-chain but ultimately rely on the security of the main chain by periodically sending a "snapshot" of the rollup's state back to Layer 1.
Layer 2 solutions considerably improve transaction speeds on Layer 1 blockchains. However, they introduce some complexity, and depending on the specific solution, security guarantees might differ from those offered by Layer 1.
The Importance of Interoperability
As the blockchain ecosystem grows, different blockchains with unique functionalities come up. Interoperability – the ability for blockchains to communicate and interact with each other – is crucial for creating a truly connected and efficient ecosystem. Currently, many blockchains operate in silos, limiting the potential for innovation and collaboration.
Layer 3 solutions aim to address these challenges by building upon the existing layered architecture. They leverage the security of Layer 1 and the scalability benefits of Layer 2 while also promoting interoperability between different blockchains.
Layer 3 – The Application Layer
Layer 3 blockchains represent the next evolutionary step in blockchain technology. Built on top of Layer 2 solutions, they function as an application layer, offering a dedicated environment for specific functionalities. This leads to the innovative concept of application-specific blockchains.
Application-Specific Blockchains
Unlike generic Layer 1 blockchains, Layer 3 allows developers to create blockchains customized to the unique needs of their dApps. For instance, a gaming dApp can leverage a Layer 3 blockchain optimized for fast microtransactions, while a DeFi application can prioritize security and complex financial operations. This level of customization allows developers to create highly efficient and user-friendly dApps.
Key Features of Layer 3 Blockchains
-
Enhanced Scalability: Layer 3 overcomes the limitations of Layer 1 by inheriting the scalability benefits of Layer 2 solutions. Additionally, Layer 3 protocols can further optimize scalability through innovative approaches:
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Layer 3 can explore alternative consensus mechanisms that are faster and more efficient than those used in Layer 1 blockchains. This can significantly increase transaction throughput.
-
Data Structures: By optimizing data storage and retrieval methods, Layer 3 blockchains can handle larger volumes of transactions without compromising on speed.
-
Interoperability: One of the primary advantages of Layer 3 is its ability to bridge communication gaps between different blockchains. This facilitates a more interconnected ecosystem where dApps can interact efficiently, regardless of the underlying blockchain they operate on. Interoperability protocols like Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) play a crucial role in enabling data and value exchange between Layer 3 blockchains built on different Layer 2 solutions.
-
Customization: As mentioned earlier, Layer 3 allows developers to tailor blockchains to their specific dApp requirements. This includes defining governance structures, transaction fees, and consensus mechanisms, allowing for highly specialized and optimized applications.
-
Security: Layer 3 inherits the security foundation established by Layer 1 blockchains. Additionally, some Layer 3 protocols may implement further security measures specific to the application's needs. However, it's crucial to remember that the overall security of a Layer 3 application depends on the security of the underlying Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions.
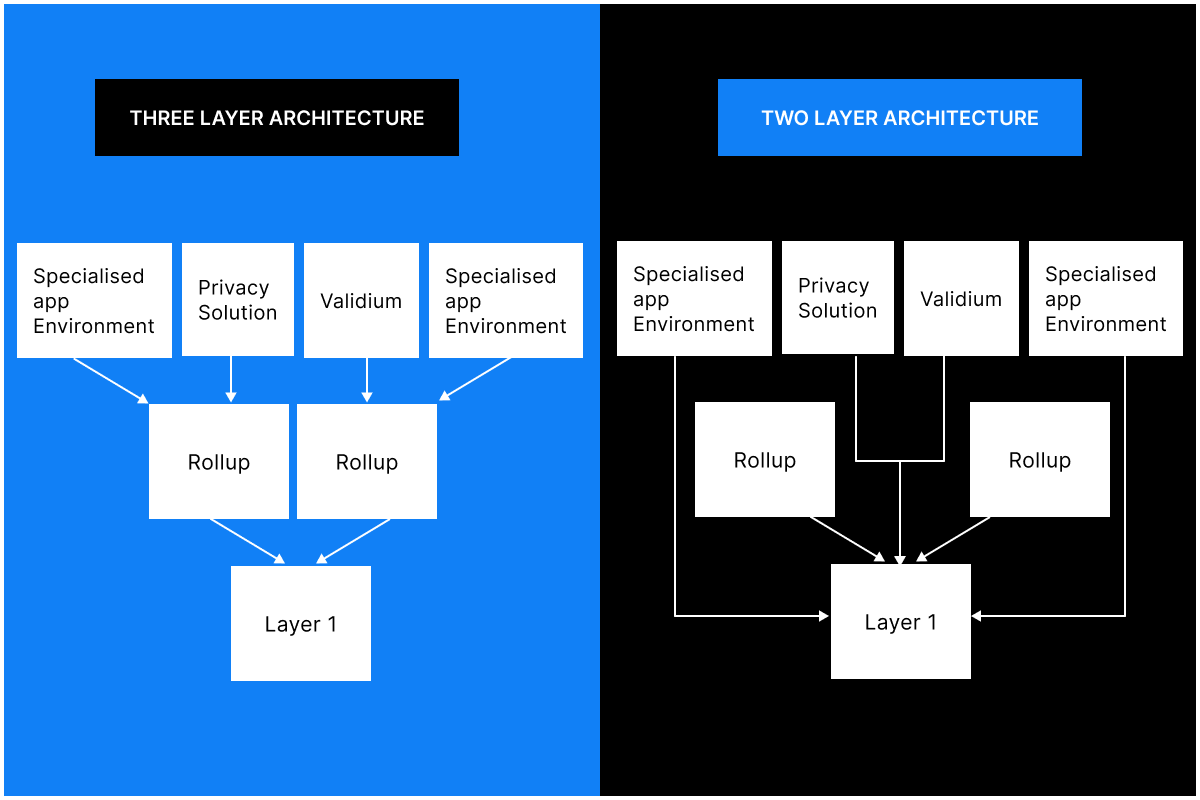
How Layer 3 Blockchains Work
Layer 3 blockchains introduce a more intricate architecture compared to Layer 1 and 2 solutions. Here's a breakdown of how they operate.
Anchoring to Layer 2
A Layer 3 blockchain doesn't operate in isolation. It anchors itself to a secure Layer 2 protocol, inheriting its security benefits. This anchoring process typically involves deploying a smart contract on the Layer 2 blockchain.
Transaction Processing
Unlike Layer 1, where every transaction is broadcast and validated on the main chain, Layer 3 allows for faster transaction processing.
-
Users interact with a dApp built on the Layer 3 blockchain.
-
Transactions are submitted to the Layer 3 network and validated according to the chosen consensus mechanism (explained further below).
-
Validated transactions are batched together into Merkle trees, a cryptographic data structure that allows for efficient verification.
State Updates and Verification
-
The Layer 3 blockchain maintains its own state, which reflects the current status of the network (e.g., user balances, application data).
-
Instead of including the entire transaction data, Layer 3 can submit a cryptographic proof (e.g., zk-SNARKs) to the underlying Layer 2 smart contract. This proof verifies the validity of the state update without revealing the underlying transaction details. This significantly reduces the data footprint on Layer 2.
-
The Layer 2 smart contract verifies the cryptographic proofs submitted by the Layer 3 blockchain.
-
If the proofs are valid, the Layer 2 smart contract updates the state of the Layer 3 blockchain on the main chain periodically. This reinforces the overall integrity of the system and allows Layer 1 to act as the ultimate arbiter in case of disputes.
Communication and Interoperability
-
Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocols (IBCs): Layer 3 networks can leverage IBCs to facilitate communication with other Layer 3 blockchains built on different Layer 2 solutions. These protocols define a standardized way for blockchains to exchange data and value securely, facilitating efficient interaction between dApps operating on separate networks.
-
Cross-Chain Transactions: With IBCs, users can initiate transactions that involve assets or data residing on different Layer 3 blockchains. The IBC translates and relays these transactions between the respective networks, ensuring secure and atomic execution (meaning either both transactions succeed or neither does).
Security Considerations
-
Inherited Security: While Layer 3 utilizes its own consensus mechanism for internal transaction validation, it ultimately relies on the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain for final settlement. Any compromise on Layer 1 or 2 can potentially impact the security of the entire system.
-
Layer 3 Specific Security Features: Some Layer 3 protocols may implement additional security measures personalized to the specific application. These could involve permissioned access controls or advanced cryptographic techniques to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Scalability Optimizations
The enhanced scalability of Layer 3 blockchains stems from several innovative technical approaches
-
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) vs. Traditional Blockchain Structures: Unlike traditional blockchains that rely on linear chains of blocks, Layer 3 can explore Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). In a DAG, transactions can reference multiple preceding transactions, creating a more flexible and scalable structure. This allows for parallel processing of transactions, significantly increasing throughput.
-
Sharding Techniques for Distributed Workload: Similar to Layer 2 solutions, Layer 3 can leverage sharding techniques to distribute the workload across multiple nodes. By partitioning the blockchain state into smaller shards, each node only needs to process a fraction of the transactions, improving overall scalability and efficiency.
-
Novel Consensus Mechanisms: Layer 3 is not limited to traditional consensus mechanisms used in Layer 1 blockchains (e.g., Proof-of-Work). It can explore faster and more efficient variations of Proof-of-Stake or Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) algorithms specifically designed for faster transaction processing in Layer 3 environments. These mechanisms can significantly reduce the time required to validate transactions, leading to faster block times and improved scalability.
Benefits of Layer 3 Blockchains
The innovative architecture of Layer 3 blockchains offers significant advantages for both developers and users within the blockchain ecosystem.
Developer Benefits
-
Faster Development Cycles
Layer 3 provides a pre-built foundation with functionalities tailored for specific application types. This eliminates the need for developers to reinvent the wheel when building dApps, saving them valuable time and resources. Furthermore, application-specific blockchains allow developers to focus on core functionalities without getting bogged down by generic Layer 1 limitations.
-
Streamlined DApp Creation
With Layer 3, developers can leverage features and functionalities specifically designed for their dApp's category (e.g., DeFi, gaming). This allows for more efficient development processes, leading to faster time-to-market and a more competitive edge.
-
Reduced Development Costs
Processing transactions on Layer 1 can be expensive due to limited scalability. Layer 3, by inheriting scalability from Layer 2, allows for faster and more cost-effective transaction processing. This leads to considerable cost savings for developers, making dApp development more accessible.
User Benefits
-
Faster and Cheaper Transactions
Transactions within dApps built on Layer 3 blockchains are significantly faster and cheaper compared to Layer 1. This translates to a smoother and more efficient user experience, with minimal wait times and lower transaction fees.
-
Wider Range of Specialized dApps
Layer 3 promotes the creation of a diverse range of dApps with specialized functionalities. Users gain access to innovative applications personalized to their specific needs, whether it's high-speed gaming transactions, complex DeFi operations, or secure data storage solutions.
-
Improved User Experience
Faster transaction processing, lower fees, and application-specific features all contribute to a more efficient and enjoyable user experience. Layer 3 leads to the creation of dApps that are truly user-friendly and accessible to a wider audience.
-
Improved Mass Adoption
Apart from the above-mentioned developer and user-specific benefits, Layer 3 blockchains can boost mass adoption of blockchain. This is because the combined benefits of scalability, security, and interoperability create a fertile ground for mass adoption of dApps. Faster transaction speeds, lower costs, and a wider range of dApps catering to diverse needs will entice users and developers alike. Layer 3 has the potential to bridge the gap between the promise of blockchain technology and widespread adoption.
Real-World Use Cases of Layer 3 Blockchains
The potential applications of Layer 3 blockchains are not limited to theoretical benefits. Here are some real-world use cases that showcase the transformative power of Layer 3 across various industries.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications built on Layer 3 can offer significantly faster and cheaper financial transactions compared to traditional DeFi protocols. This facilitates features like instant loan approvals, real-time margin trading, and hassle-free cross-border payments, transforming the DeFi space.
Blockchain Gaming
The complex in-game economies of play-to-earn and metaverse games often face scalability bottlenecks on Layer 1. Layer 3 blockchains offer a solution by enabling faster microtransactions for in-game purchases, smoother asset trading, and real-time interactions within virtual worlds, thereby, creating a more immersive and efficient gaming experience for users.
Supply Chain Management
Layer 3 can revolutionize supply chain management by improving transparency and traceability of goods. Real-time tracking of products throughout the supply chain, secure data exchange between stakeholders, and automated verification of product provenance can all be achieved using Layer 3 blockchains. This can considerably reduce inefficiencies, improve trust within the supply chain ecosystem, and combat counterfeiting.
These are just a few examples, and the possibilities are constantly evolving as Layer 3 technology matures. Potential future applications include:
-
Social Media Platforms: Decentralized social networks built on Layer 3 can provide users with greater control over their data and privacy.
-
The Internet of Things (IoT): Secure and efficient communication between a large network of connected devices can be facilitated by Layer 3 blockchains.
-
Identity Management: Layer 3 can allow for secure and self-sovereign identity management solutions, giving users control over their digital identities.
Current State & Future of Layer 3 Blockchains
While Layer 3 technology is still in its early stages of development, there are already several exciting projects pushing the boundaries.
-
Cosmos leverages its IBC protocol to facilitate communication between different blockchains, laying the groundwork for a more interconnected ecosystem.
-
Polkadot utilizes a unique sharding architecture, allowing for parallel processing of transactions across multiple parachains (application-specific blockchains).
-
dYdX is a Layer 3 decentralized exchange built on StarkNet, offering high-speed and low-cost trading experiences.
Furthermore, ongoing research is actively exploring advancements in consensus mechanisms, data structures, and security protocols specifically crafted for Layer 3 environments.
Layer 3 can help individuals and businesses make the most of the multitude of benefits that blockchain technology has to offer. It promises a future where blockchain applications are innovative as well as accessible and user-friendly for everyone.
At Codezeros, we are actively exploring the potential of Layer 3 blockchains. We believe this technology can revolutionize various industries and empower users. If you're a developer or entrepreneur interested in building on Layer 3, we encourage you to reach out to us. We'd love to collaborate and explore the possibilities together!
Post Author

Explore Deep's insightful blog posts that help businesses stay ahead of the curve, explore new possibilities, and unlock the full potential of blockchain technology
Gain a competitive edge by implementing Layer 3 solutions for your specific industry needs.
Layer 3 blockchains are the future! Implement industry-specific layer 3 blockchain solutions with Codezeros and gain a competitive edge through faster and lower costs.



