SHARE THIS ARTICLE
The Rise of Modular Blockchains and Their Benefits for Web3 Development

In the relentless pursuit of innovation within the blockchain space, a significant evolution has emerged with the rise of modular blockchains. As the demand for blockchains grew, developers faced mounting challenges with traditional monolithic architectures. These structures, while revolutionary in their inception, have inherent drawbacks in terms of scalability, flexibility, and adaptability to diverse use cases.
Recognizing these shortcomings, the need for a more agile and customizable approach to blockchain development became apparent. Thus, the trend towards modular blockchains gained momentum, offering a solution that addresses the drawbacks of monolithic architectures while paving the way for improved scalability, interoperability, and innovation within the Web3 ecosystem.
This blog will take you through the journey of modular blockchains, from the problem statement that motivated their creation, to the current state and future potential of this trend, and how modular blockchains can overcome the challenges and unlock the opportunities in Web3 development services.
Understanding Monolithic and Modular Blockchains
Depending on how blockchains handle the core tasks of the blockchain, such as consensus, data storage, smart contracts, and identity, there are two main types of blockchains – Monolithic and Modular.
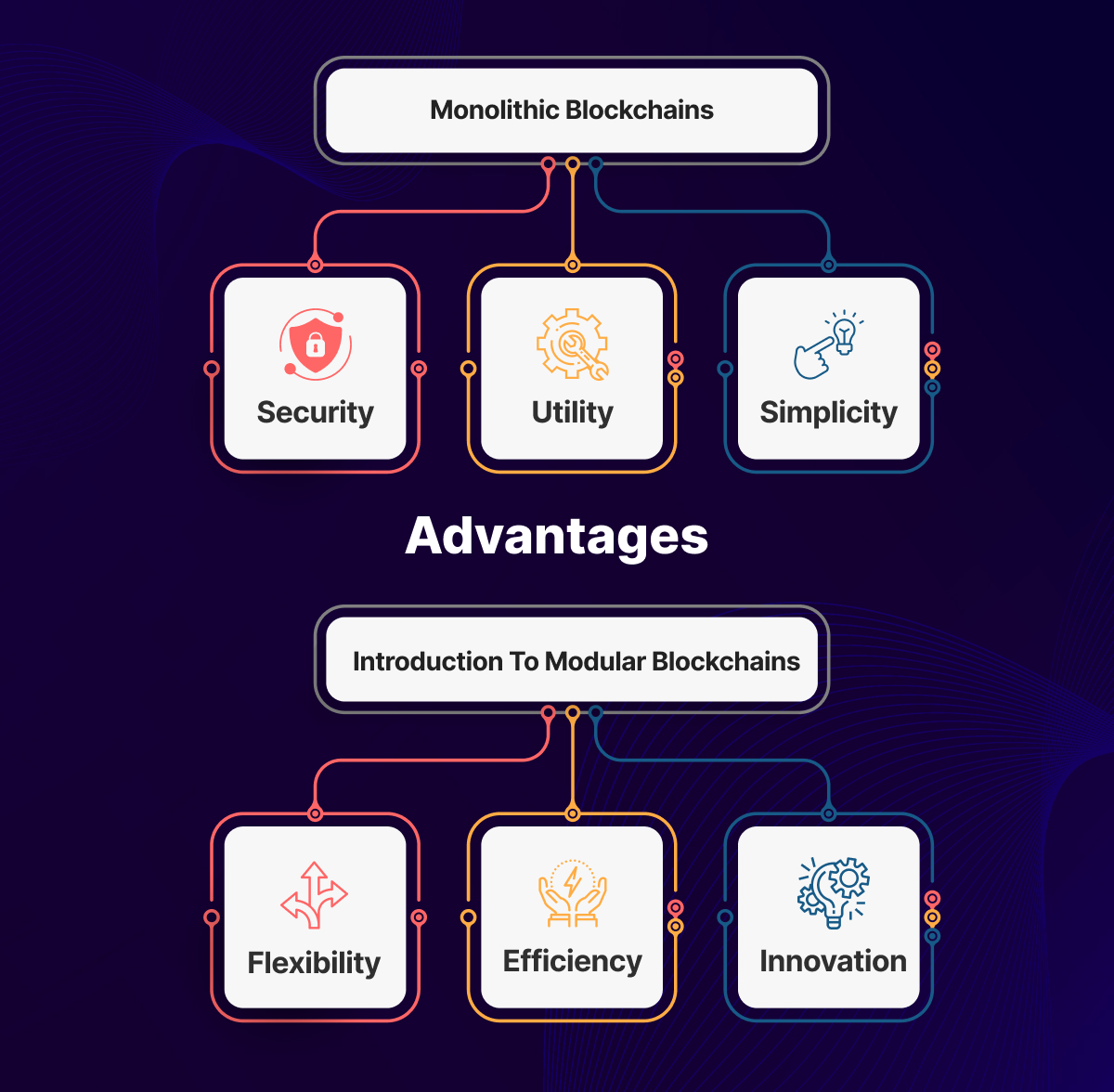
Monolithic Blockchains
Monolithic blockchains, often referred to as first-generation blockchains, are characterized by their single-layered architecture where all components, including consensus mechanisms, smart contracts, and data storage, are tightly integrated into a single system. In essence, monolithic blockchains operate as cohesive units, where all tasks are handled on the same layer.
This design has its advantages, including security, utility, and simplicity. However, as the number of users, transactions, and dApps grows, monolithic blockchains face increasing challenges and limitations, as they lack the flexibility to adapt and scale efficiently in response to evolving needs.
Characteristics of monolithic blockchains:
-
Security: Monolithic blockchains are generally considered to be more secure, as they rely on a single and consistent set of rules and protocols to validate transactions and data. Furthermore, a large and diverse network of nodes makes them more resilient to attacks and censorship.
-
Utility: These blockchains offer a wide range of features and functionalities, such as native tokens, smart contracts, governance, and interoperability.
-
Simplicity: With monolithic blockchains, users and developers do not need to deal with multiple layers or components. Moreover, a well-established and standardized development environment and community make them more accessible and reliable.
Examples of monolithic blockchains include Bitcoin, Ethereum 1.0, Solana, etc.
Introduction to Modular Blockchains
In contrast to their monolithic counterparts, modular blockchains represent a more flexible and customizable approach to Web3 development. These second-generation blockchains are designed with a modular architecture, where different components are decoupled and can be developed, deployed, and updated independently. Modular blockchains embrace the principles of modularity and interoperability, allowing developers to mix and match various modules to suit specific use cases and requirements, without compromising on other aspects of the blockchain.
Characteristics of Modular Blockchains:
-
Flexibility: Modular blockchains can adapt and evolve to changing needs and challenges, without affecting the stability and security of the underlying layer.
-
Efficiency: They can leverage the resources and capabilities of the underlying layer while reducing the congestion and costs on the network.
-
Innovation: Modular blockchains can explore new and novel solutions for blockchain applications, without being constrained by the limitations and trade-offs of the underlying layer.
Examples of modular blockchains include Polygon, Polkadot, Cosmos, etc.
Key differences between monolithic and modular blockchains
As we have seen, monolithic and modular blockchains have different designs, features, and functionalities. They also have different advantages and disadvantages, depending on the use case and perspective
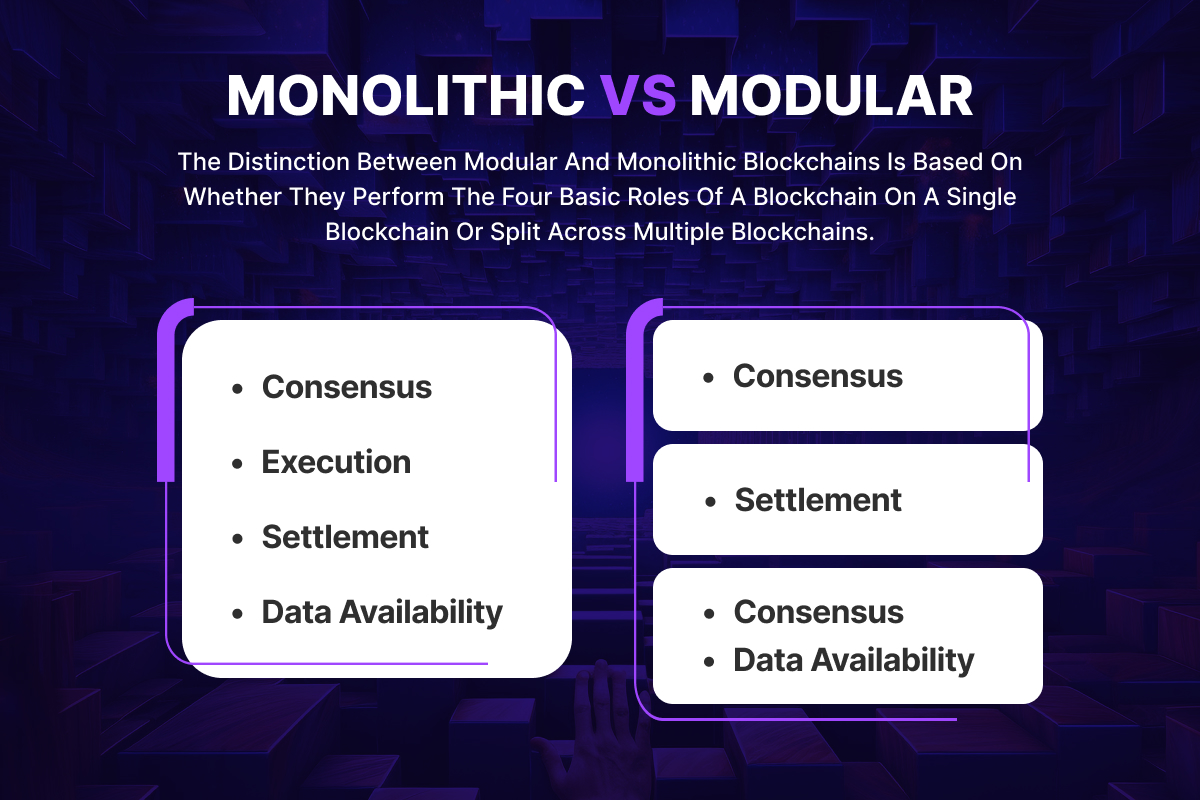
-
Architecture:
Monolithic blockchains feature a single-layered architecture, whereas modular blockchains adopt a modular design with distinct layers for consensus, smart contracts, and data storage.
-
Flexibility:
Monolithic blockchains offer limited flexibility due to their integrated structure, whereas modular blockchains provide greater flexibility by allowing developers to customize and upgrade individual components without affecting the entire system.
-
Scalability:
Monolithic blockchains may encounter scalability challenges as the entire system scales as a unit, whereas modular blockchains can achieve scalability through the independent scaling of modular components.
-
Interoperability:
Monolithic blockchains may lack interoperability with other blockchain networks, whereas modular blockchains facilitate interoperability by allowing for effortless integration with external modules and protocols.
-
Development Lifecycle:
Monolithic blockchains often require extensive development efforts for system-wide updates, whereas modular blockchains enable a more agile development lifecycle with faster deployment and updates of individual modules.
Limitations of Monolithic Blockchains
Let’s understand why we need to switch to modular blockchains for more efficient Web3 development by underscoring the most prominent limitations of monolithic blockchains.
Lack of Scalability and Performance Issues
Monolithic blockchains often face scalability challenges as they grow in size and usage. Since all components are tightly integrated, increasing transaction throughput becomes cumbersome, leading to network congestion and slower transaction processing times. As a result, monolithic blockchains may struggle to support a high volume of transactions efficiently, thereby hindering their scalability potential.
For instance, Ethereum 1.0 can only process about 15 transactions per second. This is far too low to support the growing demand and usage of blockchain applications, especially in the Web3 context, where users expect fast and seamless interactions.
Limited Flexibility and Customization Options
The integrated nature of monolithic blockchains restricts developers' ability to customize and tailor specific features according to their requirements. Any modifications or updates to the blockchain's functionality typically require changes to the entire system. This makes it challenging to introduce new features or adapt to evolving use cases swiftly. This lack of flexibility can stifle innovation and hinder the blockchain's ability to address diverse needs within the Web3 ecosystem.
Security Vulnerabilities and Single Point of Failure
Monolithic blockchains are susceptible to security vulnerabilities and present a single point of failure due to their integrated architecture. A flaw or exploit in one component of the blockchain could potentially compromise the entire network. This leads to security breaches and data manipulation. Furthermore, the centralized nature of monolithic blockchains increases the risk of censorship and control by a single entity, undermining the core principles of decentralization and trustlessness.
For example, Bitcoin and Ethereum 1.0 use a proof-of-work consensus mechanism, which requires a lot of computational power and energy to secure the network. However, this also exposes them to the risk of 51% attacks, where a malicious actor can gain control of more than half of the network’s computing power and manipulate the transactions and data.
The Rise of Modular Blockchains
Modular blockchains are the new design of blockchains, where the core tasks of the blockchain are separated into different modules that can be customized and optimized independently. They are also known as layer-2 blockchains, as they build on top of the base layer of the blockchain network. This modular design represents a departure from the monolithic architecture and allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and interoperability, laying the foundation for a more adaptable and resilient blockchain ecosystem.
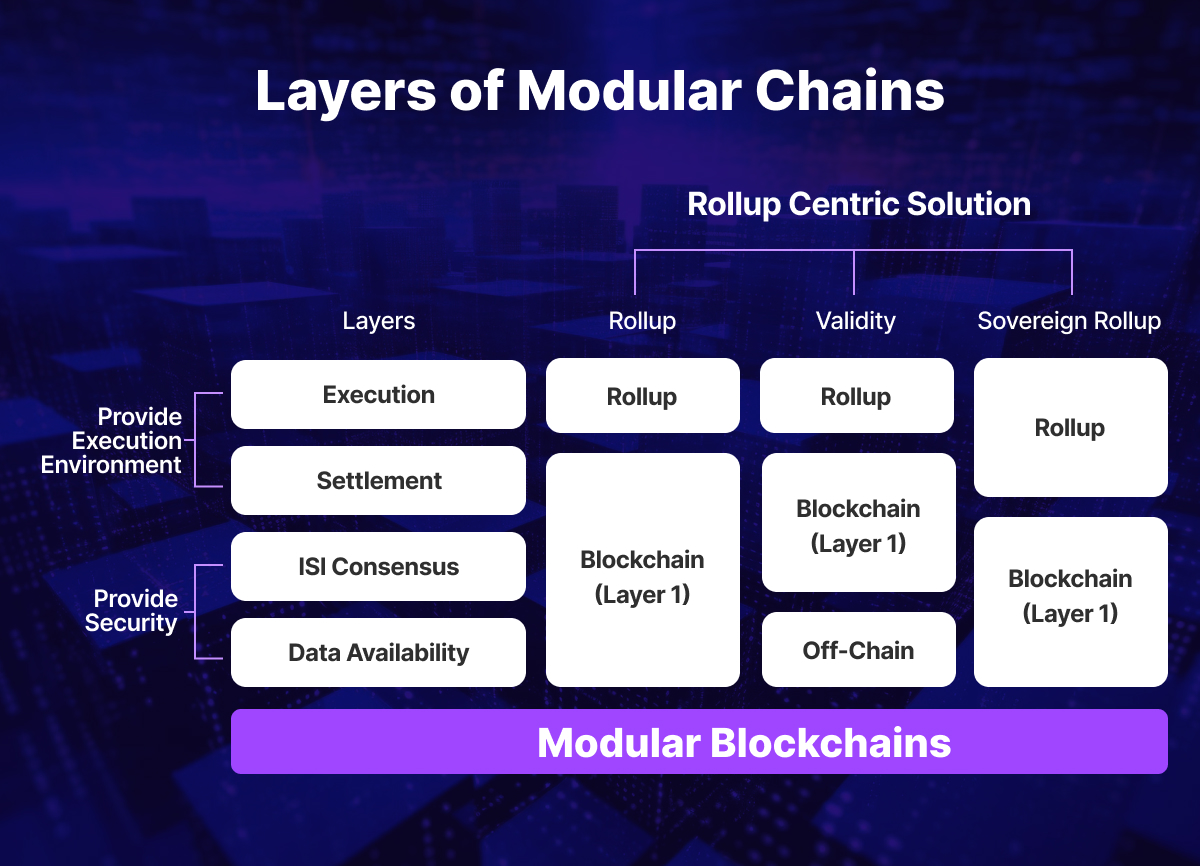
Components and Architecture of Modular Blockchains
The architecture of modular blockchains consists of distinct layers or modules, each serving a specific function within the network. These modules include the base layer, the consensus layer, the execution layer or smart contract layer, and the identity and data layer. Modular blockchains can also have additional components, such as the storage layer, the governance layer, and the application layer, depending on the specific design and implementation of the modular blockchain.
-
Base Layer: The foundation of the modular blockchain, which provides the basic security and functionality of the network. The base layer is usually a monolithic blockchain, which acts as the anchor and validator of the modular blockchain. It is responsible for maintaining the integrity and consistency of the network, and ensuring that the transactions and data are valid and authentic.
-
Consensus Layer: Responsible for achieving agreement on the state of the blockchain among network participants. The consensus layer can use different consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake, proof-of-authority, or proof-of-space, depending on the specific needs and preferences of the developers and users.
-
Execution or Smart Contract Layer: Facilitates the execution of self-executing contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on the blockchain. The execution layer is responsible for providing the functionality and logic of the network, and ensuring that the transactions and data are processed and delivered.
-
Identity and Data Layer: Uses different identity systems, such as public-key cryptography, digital signatures, or zero-knowledge proofs to manage the identities and permissions of the users and participants on the network. The data layer, on the other hand, manages the storage and retrieval of data within the blockchain, ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
Advantages of Modular Design for Web3 Development
The modular design of blockchain architectures offers several advantages for Web3 development:
-
Flexibility: Developers can mix and match different modules to create personalized solutions that meet specific use cases and requirements.
-
Scalability: Modular blockchains can scale more efficiently by independently scaling individual modules to accommodate increased transaction volume and network growth.
-
Interoperability: Modular architectures promote interoperability by facilitating the integration of external modules and protocols, facilitating efficient communication between different blockchain networks.
-
Security: Decoupling components reduces the risk of single points of failure and enhances the overall security of the blockchain network, protecting against potential exploits and vulnerabilities.
Use Cases of Modular Blockchains in Web3 Development
Modular blockchain offers a versatile foundation for a wide range of applications within the Web3 ecosystem. By providing a customizable and interoperable framework, modular blockchains allow developers to create innovative solutions that address diverse use cases across industries.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications
Modular blockchains are widely utilized in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, offering a flexible and scalable infrastructure for various financial services, including lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management. By utilizing modular components like smart contracts and decentralized oracles, DeFi platforms built on modular blockchains facilitate secure, transparent
For example, Polygon is a framework for building and connecting modular blockchains, which supports many DeFi applications, such as Aave, SushiSwap, Curve, and Balancer. Polygon allows these DeFi applications to achieve higher throughput and lower fees while maintaining the security and functionality of the underlying Ethereum network.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Digital Collectibles
Modular blockchains are instrumental in the creation and management of NFTs and digital collectibles. They provide a customizable framework for tokenization and ownership verification of unique digital assets. NFT platforms built on modular blockchains, which utilize modular smart contracts and token standards, allow creators and collectors to tokenize and trade digital art, music, gaming assets, and other digital collectibles in a decentralized and interoperable manner.
Kasuma, Unique Network, and Substrapunks are a few of many NFTs and digital collectibles on the Polkadot network, which allows them to achieve more scalability and performance, as they can leverage the resources and capabilities of the relay chain and the parachains.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Modular blockchains serve as the foundation for DAOs. They help create autonomous and transparent governance structures without centralized control. DAOs that leverage modular blockchain components like smart contracts and governance protocols allow members to participate in decision-making processes, allocate resources, and execute decentralized and transparent governance of the organization’s operations.
For instance, Cosmos, a layer2 scaling solution, allows DAOs like Aragon, DAOstack, and MolochDAO to achieve more sovereignty and customization, as they can create and manage their own zones and modules.
Supply Chain Management and Logistics
Modular blockchains are revolutionizing supply chain management and logistics by providing a transparent and immutable ledger for tracking and tracing goods throughout the supply chain. Through modular blockchain solutions, supply chain stakeholders can record and verify product perseverance, monitor inventory levels, and optimize logistic operations in a decentralized and secure manner. This enhances transparency, efficiency, and trust within the supply chain ecosystem.
Gaming and Virtual Worlds
Modular blockchains are driving innovation in the gaming and virtual worlds by providing a decentralized and interoperable infrastructure for creating, trading, and owning digital assets within virtual environments. Through modular blockchain solutions, game developers can tokenize in-game assets, enable peer-to-peer trading of virtual goods, and integrate decentralized governance mechanisms, fostering a vibrant and immersive gaming ecosystem that enhances the experience of players and content creators.
Roadblocks to Modular Blockchain Implementation
While the potential benefits of modular blockchains for Web3 development are substantial, their implementation is not without its challenges. Overcoming these roadblocks requires a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies involved in modular blockchain architecture and its integration into existing systems, along with seeking trustworthy blockchain consulting services. By addressing these challenges head-on, developers can maximize the potential of modular blockchains and drive innovation within the Web3 ecosystem.
Interoperability Standards and Protocols
Interoperability is essential for modular blockchains, as they aim to create a more connected and diverse ecosystem. However, interoperability also poses some technical and operational difficulties, as different blockchains and systems may have different designs, features, and functionalities. For instance, it is crucial for modular blockchains to ensure efficient communication and data exchange between different blockchain networks. However, this requires standardized protocols and interoperability solutions.
Developers and industry stakeholders are actively working on establishing common standards and protocols to facilitate interoperability and promote effective integration of modular blockchains with existing and emerging technologies. Some of the existing or emerging standards and protocols for interoperability are as follows.
Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC): IBC, issued by Cosmos, allows for the transfer of data and tokens across different blockchains. It is designed to be secure, reliable, and generic, and can support various types of blockchains, such as public, private, permissioned, and permissionless.
Polkadot Substrate Framework: Substrate provides a set of tools and libraries that can help developers to build and customize their own blockchains, and to connect them to the Polkadot network.
Ethereum 2.0: Ethereum 2.0, the upgraded version of Ethereum, introduces a modular design, where the network is divided into two layers: the beacon chain and the shard chains. The beacon chain is the base layer that coordinates and secures the network, while the shard chains are the execution layers that process transactions and data.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Managing regulatory compliance and governance requirements poses another challenge for modular blockchains, as regulatory frameworks vary across jurisdictions and may impact the development and adoption of decentralized applications and platforms.
Establishing clear guidelines and compliance mechanisms, while ensuring decentralized governance structures, is essential to facilitate regulatory compliance and industry adoption of modular blockchains in Web3 development.
Self-regulatory organizations (SROs): SROs are organizations that regulate and oversee the activities and conduct of their members, without direct intervention from the authorities.
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs): DAOs use smart contracts and tokens to coordinate and incentivize the actions and decisions of the members and stakeholders. They provide more democracy, transparency, and efficiency for organizational governance, such as decision-making, resource allocation, and dispute resolution.
Regulatory sandboxes: Regulatory sandboxes are frameworks that allow the testing and experimentation of new and innovative technologies and services, under a relaxed and supervised regulatory environment. They provide more flexibility, support, and feedback for the development and adoption of new and innovative technologies and services, and to identify and address the potential risks and challenges involved.
Scalability Solutions and Network Upgrades
Scalability remains a persistent challenge for blockchain networks, including modular blockchains, as the demand for transaction processing capacity continues to grow. Implementing scalable solutions, such as sharding, layer 2 protocols, and consensus mechanism optimizations, is crucial to addressing scalability challenges and ensuring the long-term viability and scalability of modular blockchains in Web3 development.
Sharding: It is a technique that divides the network into smaller and parallel units, called shards, which can process transactions and data independently and concurrently. It increases the throughput and performance of the network, as it reduces the load and increases the speed.
Rollups: Rollups aggregate and compress transactions and data on a separate layer, called the rollup layer, and periodically submit them to the underlying base layer. This reduces the congestion and costs on the network, as they offload the computation and storage from the base layer to the rollup layer.
Agglayer: It combines and synthesizes the features and functionalities of different blockchains into a single, unified layer. Agglayer provides more convenience and functionality for the users and developers, as they can access the best solutions and services from different blockchains, without switching or compromising.
Security Best Practices and Risk Management
Security remains a major concern in blockchain development, with modular blockchains facing unique security challenges due to their decentralized and modular architecture. It is essential to hire Web3 developers, who Implement robust security best practices, including code audits, formal verification, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, to reduce security risks and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data stored and processed on modular blockchains.
The Horizon of Modular Blockchain Advancement
While the potential for innovation and disruption within the Web3 ecosystem is immense, resolving the complexities of modular blockchain development requires a clear understanding of the road ahead. By identifying and addressing the challenges that lie on the horizon, we can chart a course toward a future where modular blockchains play a central role in shaping the future of a decentralized ecosystem.
Evolution of Modular Blockchain Technologies
Modular blockchain technologies are constantly evolving and improving, as they aim to provide more security, scalability, functionality, and interoperability for modular blockchains. For instance, threshold cryptography distributes the cryptographic keys and operations among multiple parties, such that a threshold number of parties is required to perform any action. It improves the security and privacy of modular blockchains, as it reduces the risk of a single point of failure, collusion, and compromise. Another example is Zero-knowledge proofs, a layer 2 solution, which enhances the efficiency and functionality of modular blockchains, as they reduce the amount of data and computation required to verify transactions and data. Then there are interoperability bridges that connect and transfer value across different blockchains and systems, using intermediate tokens or smart contracts, improving the convenience and diversity of modular blockchains, as they enable cross-chain communication and collaboration.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Modular blockchains are set to play a vital role in the integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), into the Web3 ecosystem. By providing a decentralized and interoperable infrastructure, modular blockchains offer seamless integration with AI and IoT devices, opening up new use cases and applications that leverage the combined capabilities of these technologies.
Impact on Traditional Industries and Business Models
The adoption of modular blockchains is expected to have a significant impact on traditional industries and business models, as decentralized applications and platforms built on modular blockchains disrupt existing norms and open up new opportunities for innovation and value creation. From finance to supply chain management to digital identity, modular blockchains are set to revolutionize various industries and drive the adoption of decentralized solutions in the mainstream.
Regulatory Developments and Industry Adoption
Regulatory developments and industry adoption play a crucial role in shaping the future of modular blockchains, as regulatory clarity and industry collaboration are essential for bolstering trust, promoting innovation, and driving mainstream adoption of decentralized technologies. As regulatory frameworks evolve and industry stakeholders leverage modular blockchains more consistently, we can expect to see greater adoption and integration of decentralized solutions in various sectors, fueling the growth and maturation of the Web3 ecosystem.
Building a Decentralized Future with Modular Blockchains
When it comes to Web3 development, the rise of modular blockchains signifies a vital shift, offering a modular and adaptable framework that promotes innovation and collaboration. The significance of modular design cannot be overstated, as it helps developers create customized solutions while also promoting interoperability and scalability within the blockchain ecosystem.
By utilizing modular blockchains, developers can confront new possibilities for decentralized applications and platforms. This way, they can drive forward the evolution of Web3 and provide users with greater control over their digital interactions. As we continue to explore the potential of modular blockchains, it becomes clear that their impact on Web3 development will be profound, making way for a more decentralized, transparent, and inclusive digital future.
Post Author

As a distinguished blockchain expert at Codezeros, Paritosh contributes to the company's growth by leveraging his expertise in the field. His forward-thinking mindset and deep industry knowledge position Codezeros at the forefront of blockchain advancements.
Rise of Modular Blockchains
Tap into the more agile approach of modular designs for your upcoming blockchain project. Modular blockchains are changing the game and we at Codezeros can help you harness all the benefits they offer with our unparalleled expertise in blockchain development.



