SHARE THIS ARTICLE
The Impact of the SEC's New ETF Regulation on the Market

There has been a remarkable surge in the Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF) investment in recent years. As of March 2024, the global ETF industry reached a new milestone, with assets under management totaling $12.29 trillion. This significant growth is largely driven by the popularity of equity ETFs, which account for the majority of assets at $9.6 trillion.
ETFs offer a basket of securities, typically stocks, that track a particular market index or sector. This allows investors to gain diversified exposure to a specific asset class with a single purchase. Compared to traditional mutual funds, ETFs boast several advantages. They trade on stock exchanges throughout the day, similar to individual stocks, offering greater liquidity and flexibility. Moreover, ETFs tend to have lower expense ratios than actively managed mutual funds, making them a cost-effective way to invest.
However, launching an ETF hasn't been without its challenges. Traditionally, issuers faced a cumbersome regulatory process with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that could be time-consuming and expensive. Obtaining exemptive relief, a pre-listing approval process, could take months and involve significant legal fees. This obstacle not only slowed down innovation in the ETF space but also potentially limited investor choice.
Recognizing this bottleneck, the SEC recently introduced a groundbreaking new regulation aimed at optimizing the ETF approval process. This shift in regulatory approach will impact both issuers and investors. Let's dive deeper into the specifics of this new regulation and walk through its potential consequences for the market.
Breakdown of the New Regulation
The SEC’s new regulation cuts through the red tape previously associated with ETF launches. One of the most significant changes is the elimination of exemptive relief for open-ended ETFs. This means these ETFs, which continuously create and redeem new shares based on investor demand, no longer require pre-listing approval from the SEC. This eliminates a major obstacle for issuers, saving them considerable time and legal fees associated with the application process.
However, the streamlined process comes with a new focus on transparency. Issuers are now required to disclose a range of information on their websites, including daily portfolio holdings. This provides investors with a clear picture of the underlying assets that make up the ETF, allowing them to assess the risk profile and investment strategy more effectively. Plus, investors will have access to details about the bid-ask spread, which reflects the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for an ETF share. Finally, the regulation mandates disclosure of specific data points like historical information regarding premiums and discounts on the ETf’s share price relative to its net asset value (NAV). This sheds light on the efficiency of the ETF’s creation and redemption process, allowing investors to make informed decisions about potential transaction costs.
Impact on Investors
The new regulation is expected to have a significant impact on investor confidence and market stability. One of the primary benefits for investors is increased transparency. The mandatory daily portfolio transparency requirement will provide investors with a clearer understanding of the ETF's holdings and trading activities, allowing them to make more informed investment decisions.
However, there are also potential drawbacks for investors. The increased transparency may lead to increased volatility in the market, as investors react to changes in the ETF's holdings. Additionally, the regulation may lead to higher fees for investors, as financial institutions pass on the costs of compliance to their customers.
Retail investors, who are typically less sophisticated and have limited resources, may be particularly affected by the regulation. They may struggle to understand the complex requirements and may be more susceptible to market volatility. On the other hand, institutional investors, such as pension funds and endowments, may be better equipped to adapt to the new regulatory environment and potentially benefit from increased transparency.
Impact on Financial Institutions
The new regulation will also have a significant impact on financial institutions, including brokerages and asset managers. The increased compliance costs and regulatory requirements will likely lead to higher costs for these institutions, which may be passed on to their customers.
However, the regulation may also present opportunities for financial institutions. The increased transparency and regulatory requirements may lead to a more stable and trustworthy market, which could attract more investors and increase business for financial institutions. Moreover, the regulation may lead to the development of new products and services that cater to the needs of investors in the post-regulatory environment.
Large banks and smaller brokerages may be impacted differently by the regulation. Large banks may have the resources and expertise to adapt to the new regulatory environment. Smaller brokerages, on the other hand, may struggle to comply with the new requirements and may need to reinvent their business models to remain competitive.
Market Dynamics
The streamlined approval process and reduced costs associated with launching an ETF are likely to trigger a wave of new entrants into the market. This increased competition could lead to:
-
A Surge in ETF Launches: With faster time-to-market, we can expect a rise in the number of ETF offerings catering to various investment strategies and asset classes.
-
The Rise of Niche Products: The new framework encourages innovative and niche ETFs to emerge. Previously, the lengthy approval process may have discouraged issuers from pursuing niche investment strategies due to time and resource constraints. Now, issuers can explore specialized themes or sectors with potentially lower barriers to entry.
-
Technological Tailwinds: Existing and emerging technologies will play a crucial role in empowering the creation, management, and trading of these new ETFs. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) can be utilized for portfolio construction and risk management of these novel products. Big data analytics can be utilized to identify market trends and uncover new investment opportunities, leading to the development of more targeted and efficient ETFs.
Technical Details of the Regulation
The SEC's new regulation for ETFs introduces several technical aspects that are crucial to understanding the impact on the industry. One of the key technical aspects is the use of blockchain technology and smart contracts.
Blockchain Technology and Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology and smart contracts are being increasingly used in the ETF industry to improve transparency and efficiency. Blockchain technology allows for the creation of a decentralized, distributed ledger that records all transactions and holdings in real time. This provides a secure and transparent way to track ETF holdings and trading activities.
Smart contracts, on the other hand, are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into lines of code. They can be used to automate various processes, such as the creation and redemption of ETF shares, and to ensure that the terms of the agreement are enforced.
Technical Implementation
The technical implementation of blockchain technology and smart contracts in ETFs involves several key components. First, the blockchain development companies must design the platform to handle the high volume of transactions and data that are generated by ETFs. This requires a scalable and secure platform that can handle large amounts of data and transactions.
Second, the smart contracts must be designed to automate the creation and redemption of ETF shares. This requires a deep understanding of the ETF's underlying assets and the terms of the agreement. The smart contracts must also be designed to make sure that the terms of the agreement are enforced, which requires a high degree of precision and accuracy.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
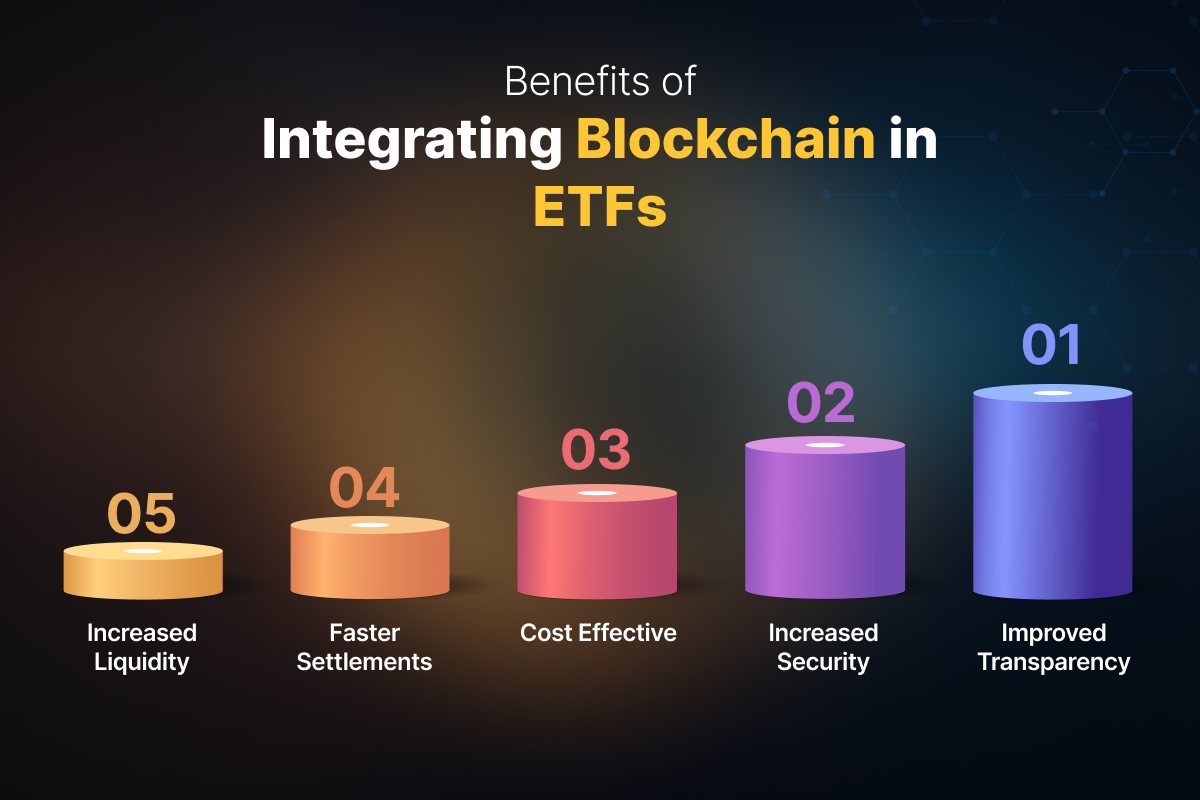
The use of blockchain technology and smart contracts in ETFs has several potential benefits, including increased transparency and the potential for higher returns. Blockchain technology provides a secure and transparent way to track ETF holdings and trading activities, which can help to increase investor confidence and reduce the risk of fraud.
Smart contracts can also help to automate various processes, such as the creation and redemption of ETF shares, which can help to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Additionally, smart contracts can help to reduce the risk of disputes and litigation.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to using blockchain development and smart contracts in ETFs. For example, the use of blockchain technology can be complex and may require significant resources to implement and maintain. Furthermore, the use of smart contracts can be limited by the complexity of the code and the potential for errors or bugs.
Examples of Blockchain Technology in ETFs
While widespread adoption is still in its early stages, there are a few examples of blockchain technology being explored within the ETF space.
-
New Thematic ETFs: Some startups are exploring the launch of new thematic ETFs focused on blockchain assets or companies. These ETFs would utilize blockchain for record-keeping and offer investors exposure to the booming blockchain industry.
-
Integration with Existing ETFs: A few existing ETF providers are exploring pilot programs to integrate certain aspects of blockchain technology into their operations. These efforts primarily focus on optimizing internal processes and improving data security.
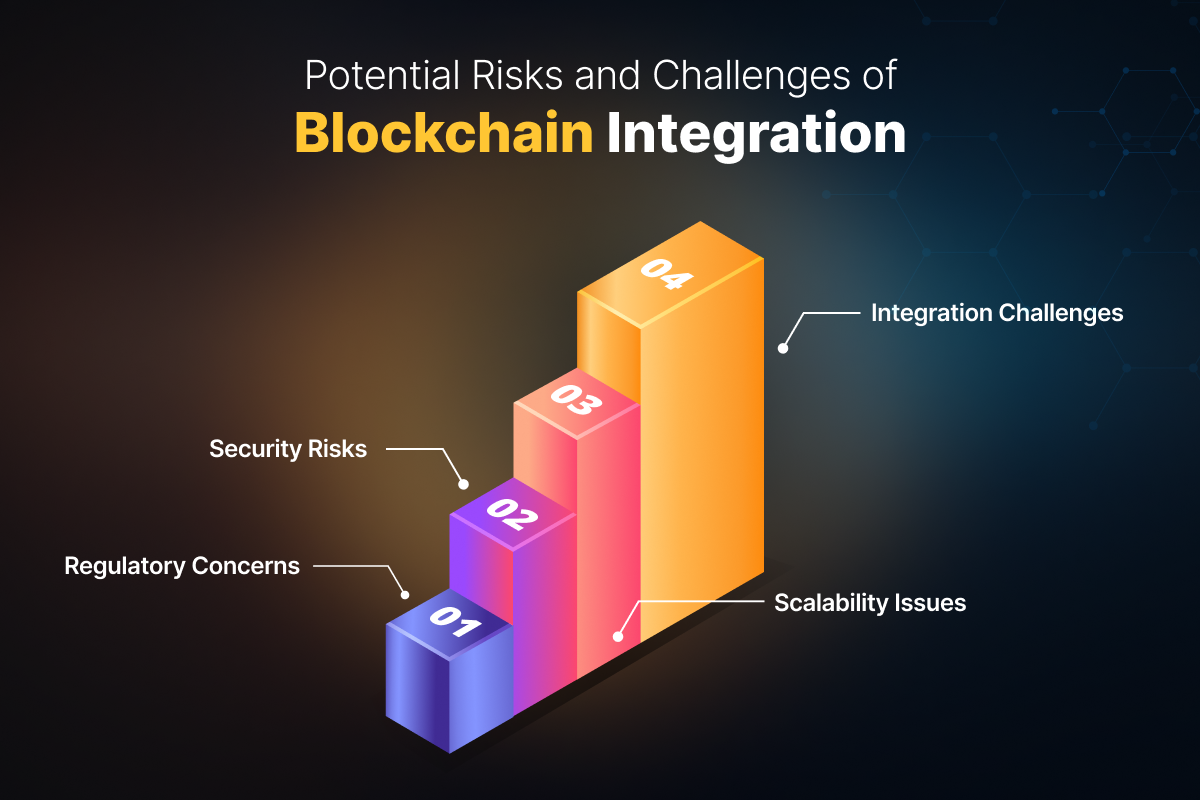
Challenges and Considerations
The SEC's new regulation marks a major shift for the ETF industry, and like any significant change, it comes with its own set of uncertainties.
Investor Education
With a potential influx of new and complex ETFs, investor education becomes essential. The responsibility lies with financial advisors as well as the issuers to provide clear and concise information about their ETFs. This includes readily available details on the underlying holdings, investment strategies, and associated risks. Investors will need to be equipped to understand the nuances of these new products to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Regulatory Scrutiny
The streamlined approval process doesn't signify a free-for-all. Regulatory scrutiny will likely shift towards ongoing monitoring of ETF activities. The SEC might focus on making sure that issuers adhere to the new transparency requirements and that the underlying investment strategies of these ETFs are consistent with their stated objectives. This continued oversight is crucial for maintaining market integrity and investor confidence.
Technological Infrastructure
The anticipated surge in ETFs will place considerable demands on technological infrastructure. Issuers will need efficient systems in place to manage the daily data collection, analysis, and disclosure mandated by the new regulations. Furthermore, the rise of more complex and niche ETFs might require advanced portfolio management and risk analysis tools. Investment in technological infrastructure will be critical for issuers to adapt and thrive in this new environment. Potential roadblocks could include the integration costs associated with new technologies and the need for skilled professionals to manage these complex systems.
The Road Ahead
The SEC's new regulations mark a turning point. While challenges like investor education and technological infrastructure needs exist, the potential for innovation and a wider array of investment options is undeniable.
The road ahead necessitates a tech-driven approach. Investors will need access to powerful research and analysis tools to sift through the growing number of ETF offerings and identify those that align with their investment goals. ETF issuers will require efficient technological solutions to manage the complexities of daily data disclosure, portfolio management, and risk analysis, particularly for niche or complex ETFs.
At Codezeros, we're a leading blockchain development company with a deep understanding of the ETF ecosystem. We're committed to developing innovative solutions that empower both investors and issuers in this new environment.
Blockchain technology holds immense potential for improving transparency and optimizing compliance within the ETF ecosystem. Our team of blockchain developers is actively exploring innovative solutions to integrate this technology into ETF management systems.
Contact us today to learn more about our suite of ETF-focused technology solutions.
Post Author
Vivek is a passionate writer and technology enthusiast with expertise in blockchain development. As the lead writer for Codezeros, he aims to educate and inform readers about the potential of blockchain technology and simplify complex concepts to present them in an engaging manner for both technical and non-technical readers.
Learn how SEC's most recent updates can impact your next blockchain project
SEC's recent updates on ETF have a far-reaching influence on the trading market, including cryptocurrency. At Codezeros, our expert consultants can help you understand its impact on your blockchain project.



